#
Storage Tables
This tutorial explains what is and how we can create a Storage Table in Azure.
A storage account can be of 3 types:
General Purpose: primarily there are 4 types of storage in this account type: Tables, Blobs, Queues, File StorageBlob Storage: optimized for Blob operations (Block Blobs or Page Blobs)File shares: optimized for sharing files in a high performant environment
In order to create Storage Tables, we need to create a General Purpose storage account.
Azure Table storage stores large amounts of structured data. The service is a NoSQL datastore which accepts authenticated calls from inside and outside the Azure cloud. Azure tables are ideal for storing structured, non-relational data.
A table is a collection of entities. Tables don't enforce a schema on entities, which means a single table can contain entities that have different sets of properties.
An entity is a set of properties, similar to a database row. An entity in Azure Storage can be up to 1MB in size. An entity in Azure Cosmos DB can be up to 2MB in size.
A property is a name-value pair. Each entity can include up to 252 properties to store data.
Each entity also has three system properties that specify a partition key, a row key, and a timestamp.
Entities with the same partition key can be queried more quickly, and inserted/updated in atomic operations.
An entity's row key is its unique identifier within a partition.
For creating a table, we can go to Azure Portal in "Storage accounts" page.
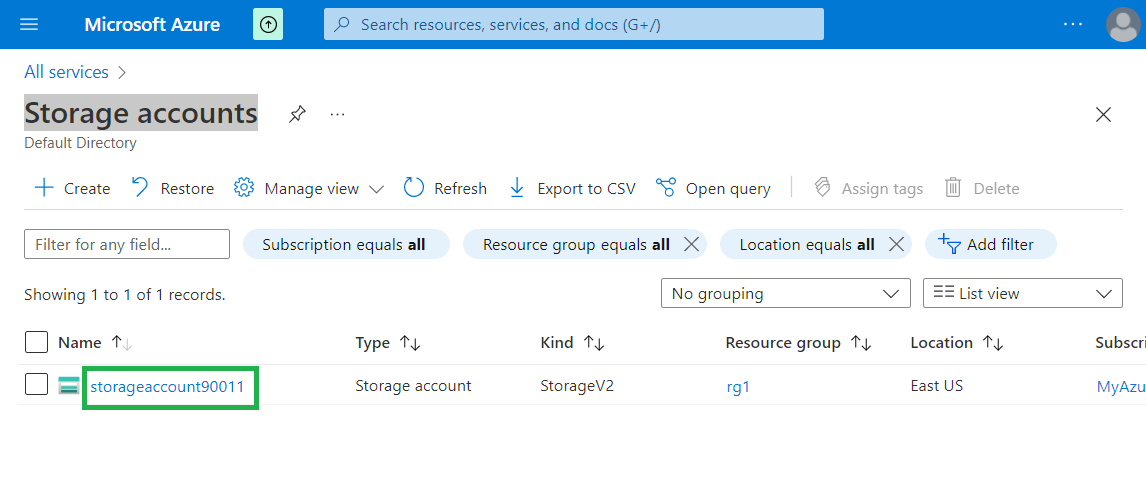
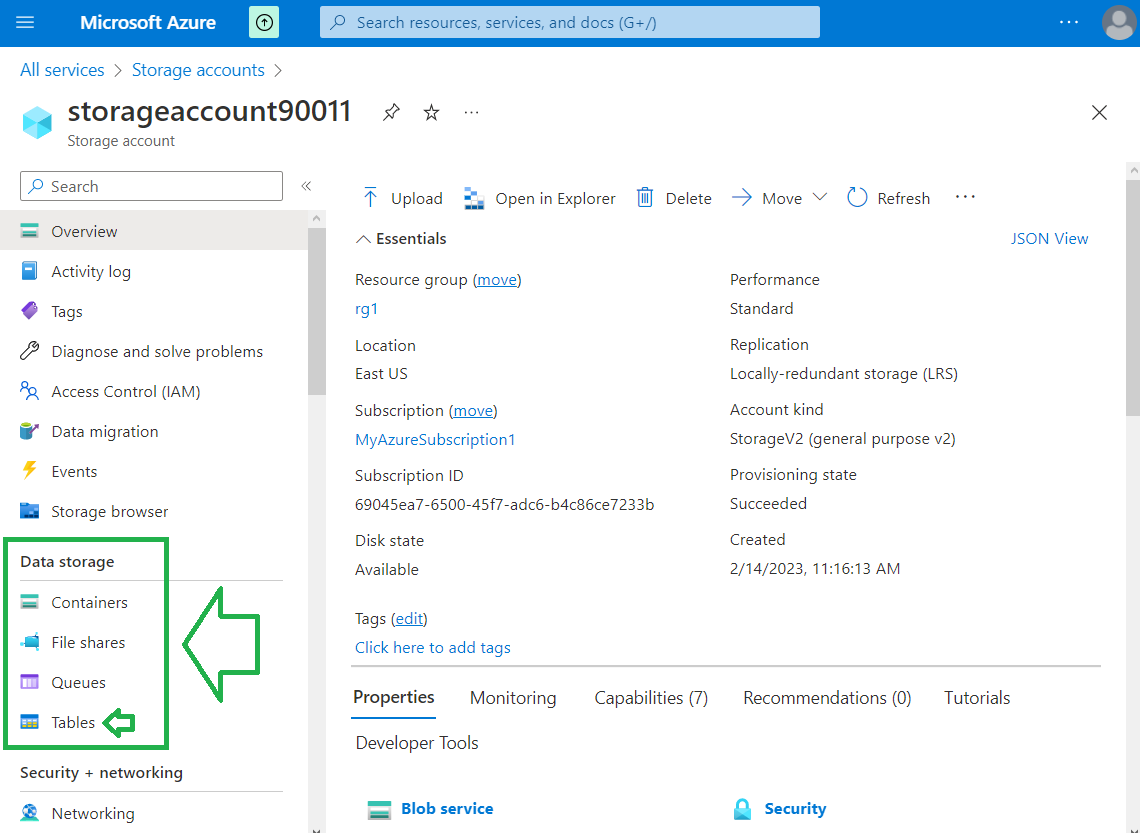
Click on Storage Account Name.
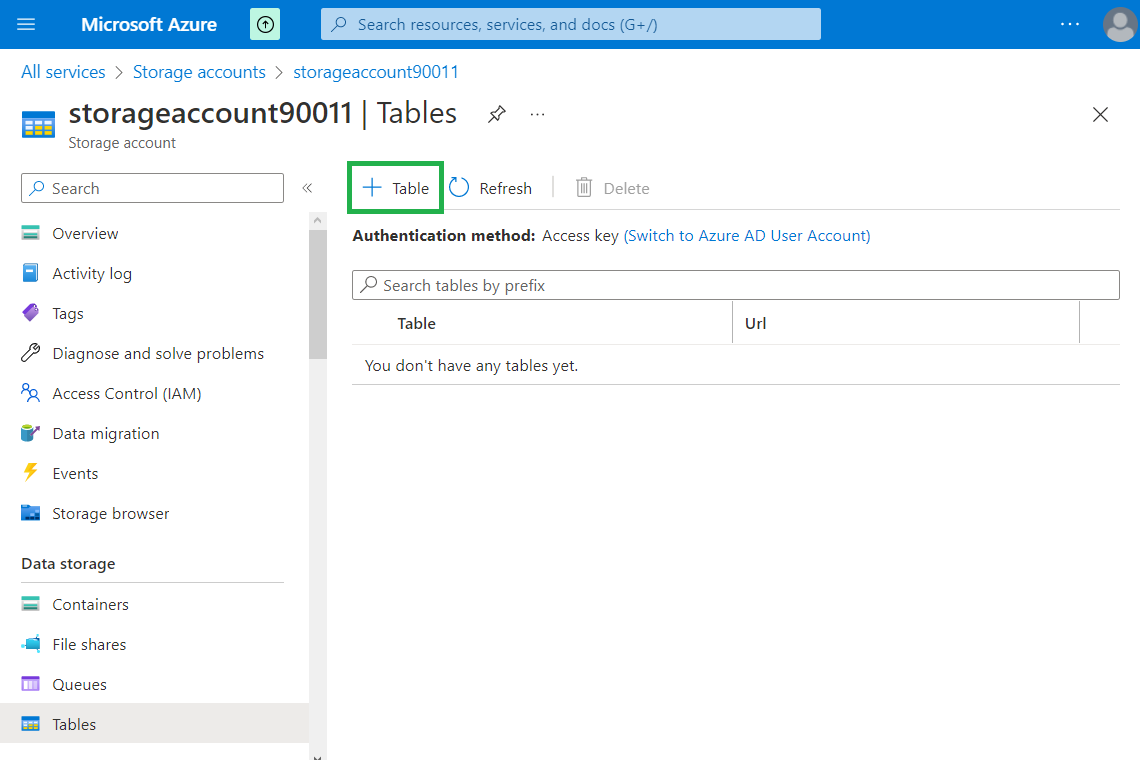
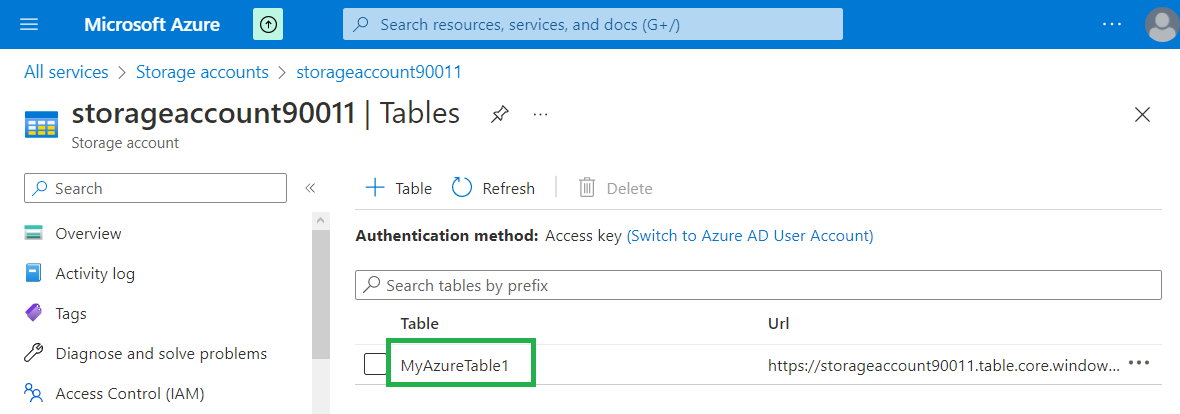
Click on "+ Table" button.
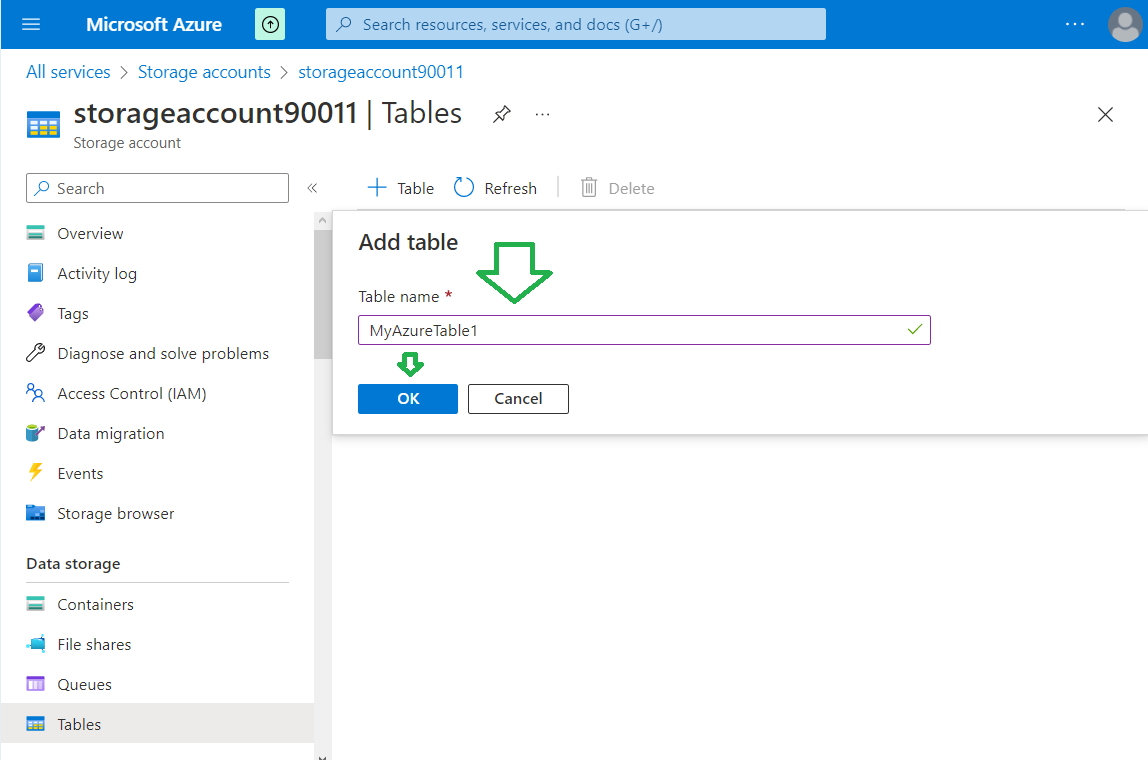
Enter a name for a table and click "OK" button. The new table will be created immediately.